PLEASE NOTE: This article is obsolete or related to a discontinued product.
Using the I2C bus
This article explains how to manage the I2C bus on the FOX Board LX
There are two ways to connect I2C chips on the FOX Board LX:
- Using the kernel driver improved by Geert Vancompernolle and implemented by default in the Phrozen SDK
- Using bit-banging routines implemented directly in the user space application
Test circuitry
|
To test both methods we've used an
I2C 8-bit A/D converter Philips PCF8591. This is a single-chip, single-supply
low power 8-bit CMOS data acquisition device with four analog inputs,
one analog output and a serial I2C-bus interface. Four trimmers are used to
change the input voltage on the four A/D chanels. The D/A channel is not used in this example.
As shown on the following table, the I2C driver uses the standard I2C data and clock lines located by Axis on PB0 and PB1 I/O lines. On the other side with the user space bit banging example the line used are IOG24 (data) and OG25 (clock). The following table shows how to connect the I2C lines on both examples:
|
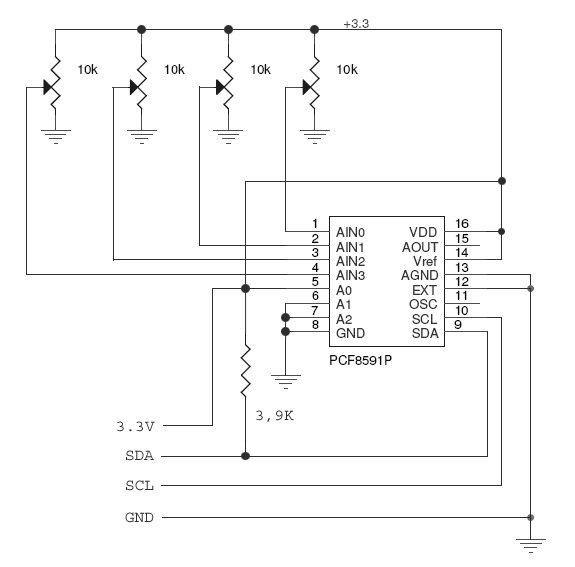
Wiring between the PCF8591 and the FOX board LX |
|||||||||||||||
Kernel driver method
This example reads the values from the four A/D channels using the I2C kernel driver and shows the voltage value to the screen://***************************************************
// pcf8591d.c
//
// Example to read A/D values from a
// 4 channel / 8 bit AD converter PCF8591
// through I2C using the I2C driver improved by
// Geert Vancompernolle
// http://www.acmesystems.it/?id=10
//***************************************************
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "sys/ioctl.h"
#include "fcntl.h"
#include "time.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "i2c_errno.h"
#include "etraxi2c.h"
int main( int argc, char **argv ) {
int rtc;
int fd_i2c;
I2C_DATA i2c_d;
int ch;
printf("Reading from a PCF8591 (4 chanel A/D at 8 bits with I2C bus)\n");
fd_i2c = open( "/dev/i2c", O_RDWR );
if (fd_i2c<=0) {
printf( "Open error on /dev/i2c\n" );
exit( 1 );
}
// PCF8591 address scheme
// | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | A2 | A1 | A0 | R/W |
i2c_d.slave =(0x09<<4)|(0x01<<1);
for (ch=0;ch<=3;ch++) {
// Select the A/D channel
i2c_d.wbuf[0] = ch;
i2c_d.wlen = 1;
if ((rtc=ioctl(fd_i2c,_IO( ETRAXI2C_IOCTYPE, I2C_WRITE), &i2c_d))!=EI2CNOERRORS) {
close(fd_i2c);
printf( "Error %d on line %d\n",rtc,__LINE__);
return ( -1 );
}
i2c_d.rlen = 3;
if ((rtc=ioctl(fd_i2c,_IO( ETRAXI2C_IOCTYPE, I2C_READ), &i2c_d))!=EI2CNOERRORS) {
close(fd_i2c);
printf( "Error %d on line %d\n",rtc,__LINE__);
return ( -1 );
}
// Show the voltage level
printf("Chanel %d = %.2fv (%02X hex)\n",ch,i2c_d.rbuf[2]*0.012941,i2c_d.rbuf[2]);
}
close(fd_i2c);
return(0);
}
To compile this code with the SDK use this makefile (see Compile a C application):
AXIS_USABLE_LIBS = UCLIBC GLIBC include $(AXIS_TOP_DIR)/tools/build/Rules.axis PROGS = pcf8591d OBJS = $(PROGS).o INSTDIR = $(prefix)/usr/bin all: $(PROGS) $(PROGS): $(OBJS) $(CC) $(LDFLAGS) $^ $(LDLIBS) -o $@ $(STRIP) $@ install: $(PROGS) $(INSTALL) -p -o root -g root -m 0777 $(PROGS) $(INSTDIR) clean: rm -f $(PROGS) *.o core test: scp $(PROGS) root@192.168.0.90:/mnt/flash
Running the example
Copy the executable file to the /mnt/flash directory and type:[root@axis /mnt/flash]103# ./pcf8591d Reading from 4 ch 8 bit A/D converter PCF8591 CH0 = 0.40v (1F hex) CH1 = 1.19v (5C hex) CH2 = 1.15v (59 hex) CH3 = 3.30v (FF hex)
User space method
This example reads the values from the four A/D channels managing from user space directly the I/O lines used for the I2C bus and shows the voltage value to the screen://***************************************************
// pcf8591nd.c
//
// Example to read A/D values from a
// 4 channel / 8 bit AD converter PCF8591
// through I2C using bit banging method in user space
// http://www.acmesystems.it/?id=10
//***************************************************
#include "stdio.h"
#include "unistd.h"
#include "sys/ioctl.h"
#include "fcntl.h"
#include "time.h"
#include "linux/gpio_syscalls.h"
#define I2C_DATA_LINE 1<<24 // IOG24 J7.21
#define I2C_CLOCK_LINE 1<<25 // OG25 J7.13
#define I2C_DATA_PORT PORTG
#define I2C_CLOCK_PORT PORTG
// Get the SDA line state
int i2c_getbit(void) {
return (gpiogetbits(I2C_DATA_PORT,I2C_DATA_LINE)?(1):(0));
}
// Set the SDA line as output
void i2c_dir_out(void) {
gpiosetdir(I2C_DATA_PORT,DIROUT,I2C_DATA_LINE);
}
// Set the SDA line as input
void i2c_dir_in(void) {
gpiosetdir(I2C_DATA_PORT,DIRIN,I2C_DATA_LINE);
}
// Set the SDA line state
void i2c_data(int state) {
if (state==1) {
i2c_dir_in();
} else {
i2c_dir_out();
gpioclearbits(I2C_DATA_PORT, I2C_DATA_LINE);
}
}
// Set the SCL line state
void i2c_clk(int state) {
if (state==1) gpiosetbits(I2C_CLOCK_PORT, I2C_CLOCK_LINE);
else gpioclearbits(I2C_CLOCK_PORT, I2C_CLOCK_LINE);
}
// Read a byte from I2C bus and send the ack sequence
// Put islast = 1 is this is the last byte to receive from the slave
unsigned char i2c_inbyte(int islast) {
unsigned char value = 0;
int bitvalue;
int i;
// Read data byte
i2c_clk(0);
i2c_dir_in();
for (i=0;i<8;i++) {
i2c_clk(1);
bitvalue = i2c_getbit();
value |= bitvalue;
if (i<7) value <<= 1;
i2c_clk(0);
}
if (islast==0) {
// Send Ack if is not the last byte to read
i2c_dir_out();
i2c_data(0);
i2c_clk(1);
i2c_clk(0);
i2c_dir_in();
} else {
// Doesn't send Ack if is the last byte to read
i2c_dir_in();
i2c_clk(1);
i2c_clk(0);
}
return value;
}
// Initializate the I2C bus
void i2c_init(void) {
i2c_dir_in();
i2c_clk(1);
}
// Send a start sequence to I2C bus
void i2c_start(void){
i2c_clk(0);
i2c_data(1);
i2c_clk(1);
i2c_data(0);
}
// Send a stop sequence to I2C bus
void i2c_stop(void) {
i2c_clk(0);
i2c_data(0);
i2c_clk(1);
i2c_data(1);
}
// Send a byte to the I2C bus and return the ack sequence from slave
// rtc
// 0 = Nack, 1=Ack
int i2c_outbyte(unsigned char x) {
int i;
int ack;
i2c_clk(0);
for (i=0;i<8;i++) {
if (x & 0x80) i2c_data(1);
else i2c_data(0);
i2c_clk(1);
i2c_clk(0);
x <<= 1;
}
i2c_dir_in();
i2c_clk(1);
ack=i2c_getbit();
i2c_clk(0);
if (ack==0) return 1;
else return 0;
}
int main(void) {
int ch;
int i2c_slave;
int ad_value;
i2c_init();
// PCF8591 address scheme
// | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | A2 | A1 | A0 | R/W |
i2c_slave =(0x09<<4)|(0x01<<1);
for (ch=0;ch<=3;ch++) {
// Select the A/D channel
i2c_start();
if (i2c_outbyte(i2c_slave|0)==0) {
printf("NACK received %d\n",__LINE__);
i2c_stop();
return -1;
}
if (i2c_outbyte(ch)==0) {
printf("NACK received %d\n",__LINE__);
i2c_stop();
return -1;
}
i2c_stop();
i2c_start();
if (i2c_outbyte(i2c_slave|1)==0) {
printf("NACK received %d\n",__LINE__);
i2c_stop();
return -1;
}
i2c_inbyte(0);
i2c_inbyte(0);
ad_value=i2c_inbyte(1);
i2c_stop();
// Show the voltage level
printf("Chanel %d = %.2fv (%02X hex)\n",ch,ad_value*0.012941,ad_value);
}
return 0;
}
To compile this code with the SDK (see Compile a C application) use the same makefile of the previous example changing this line:
PROGS = pcf8591din
PROGS = pcf8591nd
Running the example
Copy the executable file to the /mnt/flash directory and type:[root@axis /mnt/flash]103# ./pcf8591nd Reading from 4 ch 8 bit A/D converter PCF8591 CH0 = 0.40v (1F hex) CH1 = 1.19v (5C hex) CH2 = 1.15v (59 hex) CH3 = 3.30v (FF hex)
Download
- pcf8591d.c I2C sample code using I2C driver





